Nature Nanotechnology
http://www.nature.com/nnano/current_issue/rss/
Ziyue Li
Abstract
Reducing individual inflammatory factors does not always translate into clinical efficacy in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), an autoimmune disease characterized by joint inflammation. Proinflammatory M1 macrophages are a key driver of the hyperinflammatory joint microenvironment, which also promotes the progression of RA. Here we show that folate-receptor-targeted photosynthetic nanothylakoid (FA-PEG-NTK)-based phototherapy reprogrammes macrophages from M1 to anti-inflammatory M2, and successfully remodels the inflammatory RA microenvironment. The nanothylakoids were sourced from plant-derived thylakoids and developed by surface modification with distearoyl phosphoethanolamine–polyethylene glycol (PEG) via hydrophobic interactions to preserve their photocatalytic enzymes. We show that upon light irradiation in a mouse macrophage model of inflammation, the FA-PEG-NTK system generates oxygen and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, alleviating hypoxia and reducing reactive oxygen species. This rebalances the oxidative stress in M1 macrophages, thereby remodelling the inflammatory microenvironment in RA. We also show that in a collagen-induced arthritis rat model, FA-PEG-NTK-mediated phototherapy notably alleviated synovial hyperplasia and enhanced bone and cartilage regeneration, outperforming the clinical treatment methotrexate, with no apparent side effects.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
/* style specs end */
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
/* style specs start */
style {
display: none !important;
}
.LiveAreaSection * {
align-content: stretch;
align-items: stretch;
align-self: auto;
animation-delay: 0s;
animation-direction: normal;
animation-duration: 0s;
animation-fill-mode: none;
animation-iteration-count: 1;
animation-name: none;
animation-play-state: running;
animation-timing-function: ease;
azimuth: center;
backface-visibility: visible;
background-attachment: scroll;
background-blend-mode: normal;
background-clip: borderBox;
background-color: transparent;
background-image: none;
background-origin: paddingBox;
background-position: 0 0;
background-repeat: repeat;
background-size: auto auto;
block-size: auto;
border-block-end-color: currentcolor;
border-block-end-style: none;
border-block-end-width: medium;
border-block-start-color: currentcolor;
border-block-start-style: none;
border-block-start-width: medium;
border-bottom-color: currentcolor;
border-bottom-left-radius: 0;
border-bottom-right-radius: 0;
border-bottom-style: none;
border-bottom-width: medium;
border-collapse: separate;
border-image-outset: 0s;
border-image-repeat: stretch;
border-image-slice: 100%;
border-image-source: none;
border-image-width: 1;
border-inline-end-color: currentcolor;
border-inline-end-style: none;
border-inline-end-width: medium;
border-inline-start-color: currentcolor;
border-inline-start-style: none;
border-inline-start-width: medium;
border-left-color: currentcolor;
border-left-style: none;
border-left-width: medium;
border-right-color: currentcolor;
border-right-style: none;
border-right-width: medium;
border-spacing: 0;
border-top-color: currentcolor;
border-top-left-radius: 0;
border-top-right-radius: 0;
border-top-style: none;
border-top-width: medium;
bottom: auto;
box-decoration-break: slice;
box-shadow: none;
box-sizing: border-box;
break-after: auto;
break-before: auto;
break-inside: auto;
caption-side: top;
caret-color: auto;
clear: none;
clip: auto;
clip-path: none;
color: initial;
column-count: auto;
column-fill: balance;
column-gap: normal;
column-rule-color: currentcolor;
column-rule-style: none;
column-rule-width: medium;
column-span: none;
column-width: auto;
content: normal;
counter-increment: none;
counter-reset: none;
cursor: auto;
display: inline;
empty-cells: show;
filter: none;
flex-basis: auto;
flex-direction: row;
flex-grow: 0;
flex-shrink: 1;
flex-wrap: nowrap;
float: none;
font-family: initial;
font-feature-settings: normal;
font-kerning: auto;
font-language-override: normal;
font-size: medium;
font-size-adjust: none;
font-stretch: normal;
font-style: normal;
font-synthesis: weight style;
font-variant: normal;
font-variant-alternates: normal;
font-variant-caps: normal;
font-variant-east-asian: normal;
font-variant-ligatures: normal;
font-variant-numeric: normal;
font-variant-position: normal;
font-weight: 400;
grid-auto-columns: auto;
grid-auto-flow: row;
grid-auto-rows: auto;
grid-column-end: auto;
grid-column-gap: 0;
grid-column-start: auto;
grid-row-end: auto;
grid-row-gap: 0;
grid-row-start: auto;
grid-template-areas: none;
grid-template-columns: none;
grid-template-rows: none;
height: auto;
hyphens: manual;
image-orientation: 0deg;
image-rendering: auto;
image-resolution: 1dppx;
ime-mode: auto;
inline-size: auto;
isolation: auto;
justify-content: flexStart;
left: auto;
letter-spacing: normal;
line-break: auto;
line-height: normal;
list-style-image: none;
list-style-position: outside;
list-style-type: disc;
margin-block-end: 0;
margin-block-start: 0;
margin-bottom: 0;
margin-inline-end: 0;
margin-inline-start: 0;
margin-left: 0;
margin-right: 0;
margin-top: 0;
mask-clip: borderBox;
mask-composite: add;
mask-image: none;
mask-mode: matchSource;
mask-origin: borderBox;
mask-position: 0 0;
mask-repeat: repeat;
mask-size: auto;
mask-type: luminance;
max-height: none;
max-width: none;
min-block-size: 0;
min-height: 0;
min-inline-size: 0;
min-width: 0;
mix-blend-mode: normal;
object-fit: fill;
object-position: 50% 50%;
offset-block-end: auto;
offset-block-start: auto;
offset-inline-end: auto;
offset-inline-start: auto;
opacity: 1;
order: 0;
orphans: 2;
outline-color: initial;
outline-offset: 0;
outline-style: none;
outline-width: medium;
overflow: visible;
overflow-wrap: normal;
overflow-x: visible;
overflow-y: visible;
padding-block-end: 0;
padding-block-start: 0;
padding-bottom: 0;
padding-inline-end: 0;
padding-inline-start: 0;
padding-left: 0;
padding-right: 0;
padding-top: 0;
page-break-after: auto;
page-break-before: auto;
page-break-inside: auto;
perspective: none;
perspective-origin: 50% 50%;
pointer-events: auto;
position: static;
quotes: initial;
resize: none;
right: auto;
ruby-align: spaceAround;
ruby-merge: separate;
ruby-position: over;
scroll-behavior: auto;
scroll-snap-coordinate: none;
scroll-snap-destination: 0 0;
scroll-snap-points-x: none;
scroll-snap-points-y: none;
scroll-snap-type: none;
shape-image-threshold: 0;
shape-margin: 0;
shape-outside: none;
tab-size: 8;
table-layout: auto;
text-align: initial;
text-align-last: auto;
text-combine-upright: none;
text-decoration-color: currentcolor;
text-decoration-line: none;
text-decoration-style: solid;
text-emphasis-color: currentcolor;
text-emphasis-position: over right;
text-emphasis-style: none;
text-indent: 0;
text-justify: auto;
text-orientation: mixed;
text-overflow: clip;
text-rendering: auto;
text-shadow: none;
text-transform: none;
text-underline-position: auto;
top: auto;
touch-action: auto;
transform: none;
transform-box: borderBox;
transform-origin: 50% 50%0;
transform-style: flat;
transition-delay: 0s;
transition-duration: 0s;
transition-property: all;
transition-timing-function: ease;
vertical-align: baseline;
visibility: visible;
white-space: normal;
widows: 2;
width: auto;
will-change: auto;
word-break: normal;
word-spacing: normal;
word-wrap: normal;
writing-mode: horizontalTb;
z-index: auto;
-webkit-appearance: none;
-moz-appearance: none;
-ms-appearance: none;
appearance: none;
margin: 0;
}
.LiveAreaSection {
width: 100%;
}
.LiveAreaSection .login-option-buybox {
display: block;
width: 100%;
font-size: 17px;
line-height: 30px;
color: #222;
padding-top: 30px;
font-family: Harding, Palatino, serif;
}
.LiveAreaSection .additional-access-options {
display: block;
font-weight: 700;
font-size: 17px;
line-height: 30px;
color: #222;
font-family: Harding, Palatino, serif;
}
.LiveAreaSection .additional-login > li:not(:first-child)::before {
transform: translateY(-50%);
content: “”;
height: 1rem;
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 0;
border-left: 2px solid #999;
}
.LiveAreaSection .additional-login > li:not(:first-child) {
padding-left: 10px;
}
.LiveAreaSection .additional-login > li {
display: inline-block;
position: relative;
vertical-align: middle;
padding-right: 10px;
}
.BuyBoxSection {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
flex: 1;
flex-direction: row-reverse;
margin: -30px -15px 0;
}
.BuyBoxSection .box-inner {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
padding: 30px 5px;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: space-between;
}
.BuyBoxSection p {
margin: 0;
}
.BuyBoxSection .readcube-buybox {
background-color: #f3f3f3;
flex-shrink: 1;
flex-grow: 1;
flex-basis: 255px;
background-clip: content-box;
padding: 0 15px;
margin-top: 30px;
}
.BuyBoxSection .subscribe-buybox {
background-color: #f3f3f3;
flex-shrink: 1;
flex-grow: 4;
flex-basis: 300px;
background-clip: content-box;
padding: 0 15px;
margin-top: 30px;
}
.BuyBoxSection .subscribe-buybox-nature-plus {
background-color: #f3f3f3;
flex-shrink: 1;
flex-grow: 4;
flex-basis: 100%;
background-clip: content-box;
padding: 0 15px;
margin-top: 30px;
}
.BuyBoxSection .title-readcube,
.BuyBoxSection .title-buybox {
display: block;
margin: 0;
margin-right: 10%;
margin-left: 10%;
font-size: 24px;
line-height: 32px;
color: #222;
text-align: center;
font-family: Harding, Palatino, serif;
}
.BuyBoxSection .title-asia-buybox {
display: block;
margin: 0;
margin-right: 5%;
margin-left: 5%;
font-size: 24px;
line-height: 32px;
color: #222;
text-align: center;
font-family: Harding, Palatino, serif;
}
.BuyBoxSection .asia-link,
.Link-328123652,
.Link-2926870917,
.Link-2291679238,
.Link-595459207 {
color: #069;
cursor: pointer;
text-decoration: none;
font-size: 1.05em;
font-family: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, “Segoe UI”, Roboto,
Oxygen-Sans, Ubuntu, Cantarell, “Helvetica Neue”, sans-serif;
line-height: 1.05em6;
}
.BuyBoxSection .access-readcube {
display: block;
margin: 0;
margin-right: 10%;
margin-left: 10%;
font-size: 14px;
color: #222;
padding-top: 10px;
text-align: center;
font-family: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, “Segoe UI”, Roboto,
Oxygen-Sans, Ubuntu, Cantarell, “Helvetica Neue”, sans-serif;
line-height: 20px;
}
.BuyBoxSection ul {
margin: 0;
}
.BuyBoxSection .link-usp {
display: list-item;
margin: 0;
margin-left: 20px;
padding-top: 6px;
list-style-position: inside;
}
.BuyBoxSection .link-usp span {
font-size: 14px;
color: #222;
font-family: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, “Segoe UI”, Roboto,
Oxygen-Sans, Ubuntu, Cantarell, “Helvetica Neue”, sans-serif;
line-height: 20px;
}
.BuyBoxSection .access-asia-buybox {
display: block;
margin: 0;
margin-right: 5%;
margin-left: 5%;
font-size: 14px;
color: #222;
padding-top: 10px;
text-align: center;
font-family: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, “Segoe UI”, Roboto,
Oxygen-Sans, Ubuntu, Cantarell, “Helvetica Neue”, sans-serif;
line-height: 20px;
}
.BuyBoxSection .access-buybox {
display: block;
margin: 0;
margin-right: 10%;
margin-left: 10%;
font-size: 14px;
color: #222;
opacity: 0.8px;
padding-top: 10px;
text-align: center;
font-family: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, “Segoe UI”, Roboto,
Oxygen-Sans, Ubuntu, Cantarell, “Helvetica Neue”, sans-serif;
line-height: 20px;
}
.BuyBoxSection .price-buybox {
display: block;
font-size: 30px;
color: #222;
font-family: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, “Segoe UI”, Roboto,
Oxygen-Sans, Ubuntu, Cantarell, “Helvetica Neue”, sans-serif;
padding-top: 30px;
text-align: center;
}
.BuyBoxSection .price-buybox-to {
display: block;
font-size: 30px;
color: #222;
font-family: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, “Segoe UI”, Roboto,
Oxygen-Sans, Ubuntu, Cantarell, “Helvetica Neue”, sans-serif;
text-align: center;
}
.BuyBoxSection .price-info-text {
font-size: 16px;
padding-right: 10px;
color: #222;
font-family: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, “Segoe UI”, Roboto,
Oxygen-Sans, Ubuntu, Cantarell, “Helvetica Neue”, sans-serif;
}
.BuyBoxSection .price-value {
font-size: 30px;
font-family: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, “Segoe UI”, Roboto,
Oxygen-Sans, Ubuntu, Cantarell, “Helvetica Neue”, sans-serif;
}
.BuyBoxSection .price-per-period {
font-family: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, “Segoe UI”, Roboto,
Oxygen-Sans, Ubuntu, Cantarell, “Helvetica Neue”, sans-serif;
}
.BuyBoxSection .price-from {
font-size: 14px;
padding-right: 10px;
color: #222;
font-family: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, “Segoe UI”, Roboto,
Oxygen-Sans, Ubuntu, Cantarell, “Helvetica Neue”, sans-serif;
line-height: 20px;
}
.BuyBoxSection .issue-buybox {
display: block;
font-size: 13px;
text-align: center;
color: #222;
font-family: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, “Segoe UI”, Roboto,
Oxygen-Sans, Ubuntu, Cantarell, “Helvetica Neue”, sans-serif;
line-height: 19px;
}
.BuyBoxSection .no-price-buybox {
display: block;
font-size: 13px;
line-height: 18px;
text-align: center;
padding-right: 10%;
padding-left: 10%;
padding-bottom: 20px;
padding-top: 30px;
color: #222;
font-family: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, “Segoe UI”, Roboto,
Oxygen-Sans, Ubuntu, Cantarell, “Helvetica Neue”, sans-serif;
}
.BuyBoxSection .vat-buybox {
display: block;
margin-top: 5px;
margin-right: 20%;
margin-left: 20%;
font-size: 11px;
color: #222;
padding-top: 10px;
padding-bottom: 15px;
text-align: center;
font-family: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, “Segoe UI”, Roboto,
Oxygen-Sans, Ubuntu, Cantarell, “Helvetica Neue”, sans-serif;
line-height: 17px;
}
.BuyBoxSection .tax-buybox {
display: block;
width: 100%;
color: #222;
padding: 20px 16px;
text-align: center;
font-family: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, “Segoe UI”, Roboto,
Oxygen-Sans, Ubuntu, Cantarell, “Helvetica Neue”, sans-serif;
line-height: NaNpx;
}
.BuyBoxSection .button-container {
display: flex;
padding-right: 20px;
padding-left: 20px;
justify-content: center;
}
.BuyBoxSection .button-container > * {
flex: 1px;
}
.BuyBoxSection .button-container > a:hover,
.Button-505204839:hover,
.Button-1078489254:hover,
.Button-2737859108:hover {
text-decoration: none;
}
.BuyBoxSection .btn-secondary {
background: #fff;
}
.BuyBoxSection .button-asia {
background: #069;
border: 1px solid #069;
border-radius: 0;
cursor: pointer;
display: block;
padding: 9px;
outline: 0;
text-align: center;
text-decoration: none;
min-width: 80px;
margin-top: 75px;
}
.BuyBoxSection .button-label-asia,
.ButtonLabel-3869432492,
.ButtonLabel-3296148077,
.ButtonLabel-1636778223 {
display: block;
color: #fff;
font-size: 17px;
line-height: 20px;
font-family: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, “Segoe UI”, Roboto,
Oxygen-Sans, Ubuntu, Cantarell, “Helvetica Neue”, sans-serif;
text-align: center;
text-decoration: none;
cursor: pointer;
}
.Button-505204839,
.Button-1078489254,
.Button-2737859108 {
background: #069;
border: 1px solid #069;
border-radius: 0;
cursor: pointer;
display: block;
padding: 9px;
outline: 0;
text-align: center;
text-decoration: none;
min-width: 80px;
max-width: 320px;
margin-top: 20px;
}
.Button-505204839 .btn-secondary-label,
.Button-1078489254 .btn-secondary-label,
.Button-2737859108 .btn-secondary-label {
color: #069;
}
.uList-2102244549 {
list-style: none;
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
.article-buy-button {
font-family: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, “Segoe UI”, Roboto, Oxygen-Sans, Ubuntu, Cantarell, “Helvetica Neue”, sans-serif;
color: #069;
}
/* style specs end */
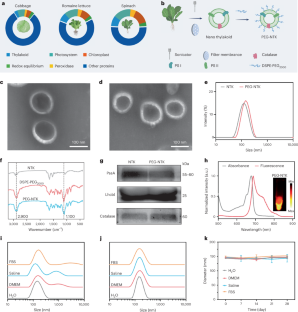
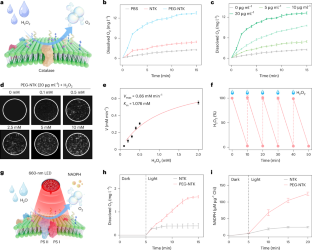
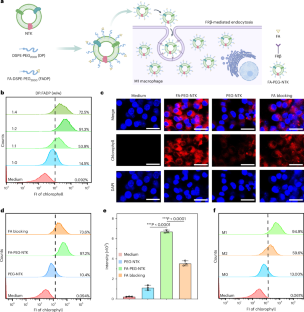
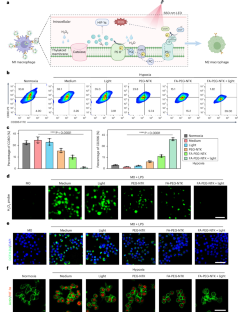

Data availability
All the data supporting the findings of this study are presented in the Article and its Supplementary Information. The bulk transcriptome and single-cell RNA sequencing data generated in this study have been deposited in the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) under the BioProject accession number PRJNA1312955 and PRJNA1314299. The proteomics data have been deposited in the iProX database under accession number IPX0013257000. Source data are provided with this paper.
References
-
Aletaha, D. & Smolen, J. S. Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis: a review. JAMA 320, 1360–1372 (2018).
-
Gravallese, E. M. & Firestein, G. S. Rheumatoid arthritis—common origins, divergent mechanisms. N. Engl. J. Med. 388, 529–542 (2023).
-
Zhang, F. et al. Deconstruction of rheumatoid arthritis synovium defines inflammatory subtypes. Nature 623, 616–624 (2023).
-
Fearon, U., Hanlon, M. M., Floudas, A. & Veale, D. J. Cellular metabolic adaptations in rheumatoid arthritis and their therapeutic implications. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 18, 398–414 (2022).
-
Buckley, C. D., Ospelt, C., Gay, S. & Midwood, K. S. Location, location, location: how the tissue microenvironment affects inflammation in RA. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 17, 195–212 (2021).
-
Weyand, C. M. & Goronzy, J. J. Immunometabolism in early and late stages of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 13, 291–301 (2017).
-
Boutet, M. A. et al. Novel insights into macrophage diversity in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Autoimmun. Rev. 20, 102758 (2021).
-
Martel-Pelletier, J. et al. Osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2, 16072 (2016).
-
Burmester, G. R. & Pope, J. E. Novel treatment strategies in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 389, 2338–2348 (2017).
-
Nissen, S. E. et al. Cardiovascular safety of celecoxib, naproxen, or ibuprofen for arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 375, 2519–2529 (2016).
-
Erhardt, D. P. et al. Low persistence rates in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with triple therapy and adverse drug events associated with sulfasalazine. Arthritis Care Res. 71, 1326–1335 (2019).
-
Zhu, Y. et al. Rheumatoid arthritis microenvironment insights into treatment effect of nanomaterials. Nano Today 42, 101358 (2022).
-
Nizet, V. & Johnson, R. S. Interdependence of hypoxic and innate immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 9, 609–617 (2009).
-
Zhao, Y. et al. Nanozyme-reinforced hydrogel as a H2O2-driven oxygenerator for enhancing prosthetic interface osseointegration in rheumatoid arthritis therapy. Nat. Commun. 13, 6758 (2022).
-
Zhang, Q. et al. Neutrophil membrane-coated nanoparticles inhibit synovial inflammation and alleviate joint damage in inflammatory arthritis. Nat. Nanotechnol. 13, 1182–1190 (2018).
-
Jia, M. et al. Messenger nanozyme for reprogramming the microenvironment of rheumatoid arthritis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 15, 338–353 (2023).
-
Kim, J. et al. Synergistic oxygen generation and reactive oxygen species scavenging by manganese ferrite/ceria co-decorated nanoparticles for rheumatoid arthritis treatment. ACS Nano 13, 3206–3217 (2019).
-
Yang, Y. et al. Targeted silver nanoparticles for rheumatoid arthritis therapy via macrophage apoptosis and re-polarization. Biomaterials 264, 120390 (2021).
-
Yang, J., Yang, B. & Shi, J. A nanomedicine-enabled ion-exchange strategy for enhancing curcumin-based rheumatoid arthritis therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 62, e202310061 (2023).
-
Xu, C. et al. Arthritic microenvironment actuated nanomotors for active rheumatoid arthritis therapy. Adv. Sci. 10, e2204881 (2023).
-
Chen, J. et al. Photoacoustic image-guided biomimetic nanoparticles targeting rheumatoid arthritis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 119, e2213373119 (2022).
-
Koo, S. et al. Ceria-vesicle nanohybrid therapeutic for modulation of innate and adaptive immunity in a collagen-induced arthritis model. Nat. Nanotechnol. 18, 1502–1514 (2023).
-
Del Giudice, G. et al. An ancestral molecular response to nanomaterial particulates. Nat. Nanotechnol. 18, 957–966 (2023).
-
Stater, E. P., Sonay, A. Y., Hart, C. & Grimm, J. The ancillary effects of nanoparticles and their implications for nanomedicine. Nat. Nanotechnol. 16, 1180–1194 (2021).
-
Gao, J. et al. Intracerebral fate of organic and inorganic nanoparticles is dependent on microglial extracellular vesicle function. Nat. Nanotechnol. 19, 376–386 (2024).
-
Li, Y. et al. Innate immunity-modulating nanobiomaterials for controlling inflammation resolution. Matter 7, 3811–3844 (2024).
-
Zhang, M. et al. Edible ginger-derived nanoparticles: a novel therapeutic approach for the prevention and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease and colitis-associated cancer. Biomaterials 101, 321–340 (2016).
-
Chen, Q. et al. Natural exosome-like nanovesicles from edible tea flowers suppress metastatic breast cancer via ROS generation and microbiota modulation. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 12, 907–923 (2022).
-
Feng, T., Ahmed, W., Ahmed, T. & Chen, L. Nanoparticles derived from herbal preparations may represent a novel nucleic acid therapy. Interdiscip. Med. 2, e20230029 (2024).
-
Miller, T. E. et al. Light-powered CO2 fixation in a chloroplast mimic with natural and synthetic parts. Science 368, 649–654 (2020).
-
Gao, F. et al. Artificial photosynthetic cells with biotic–abiotic hybrid energy modules for customized CO2 conversion. Nat. Commun. 14, 6783 (2023).
-
Hou, L. et al. Hybrid-membrane-decorated Prussian blue for effective cancer immunotherapy via tumor-associated macrophages polarization and hypoxia relief. Adv. Mater. 34, e2200389 (2022).
-
Suk, J. S., Xu, Q., Kim, N., Hanes, J. & Ensign, L. M. PEGylation as a strategy for improving nanoparticle-based drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 99, 28–51 (2016).
-
Kobayashi, K., Jimbo, H., Nakamura, Y. & Wada, H. Biosynthesis of phosphatidylglycerol in photosynthetic organisms. Prog. Lipid Res. 93, 101266 (2024).
-
Pali, T., Garab, G., Horvath, L. I. & Kota, Z. Functional significance of the lipid-protein interface in photosynthetic membranes. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 60, 1591–1606 (2003).
-
Liu, J. et al. Delivery of biomimetic liposomes via meningeal lymphatic vessels route for targeted therapy of Parkinson’s disease. Research 6, 0030 (2023).
-
Hao, M. et al. Combination of metabolic intervention and T cell therapy enhances solid tumor immunotherapy. Sci. Transl. Med. 12, eaaz6667 (2020).
-
Barber, J. A mechanism for water splitting and oxygen production in photosynthesis. Nat. Plants 3, 17041 (2017).
-
Kafri, M. et al. Systematic identification and characterization of genes in the regulation and biogenesis of photosynthetic machinery. Cell 186, 5638–5655.25 (2023).
-
Hald Albertsen, C. et al. The role of lipid components in lipid nanoparticles for vaccines and gene therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 188, 114416 (2022).
-
Chen, P. et al. A plant-derived natural photosynthetic system for improving cell anabolism. Nature 612, 546–554 (2022).
-
Alivernini, S. et al. Distinct synovial tissue macrophage subsets regulate inflammation and remission in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Med. 26, 1295–1306 (2020).
-
Smolen, J. S. et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 4, 18001 (2018).
-
Lan, R. et al. Folate receptor-targeted NIR-II dual-model nanoprobes for multiscale visualization of macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis. Adv. Func. Mat. 33, 2300342 (2023).
-
Ma, Y. et al. DNA origami as a nanomedicine for targeted rheumatoid arthritis therapy through reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide scavenging. ACS Nano 16, 12520–12531 (2022).
-
Hegarty, L. M., Jones, G. R. & Bain, C. C. Macrophages in intestinal homeostasis and inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 20, 538–553 (2023).
-
Venkatesan, R. et al. Immuno-modulating theranostic gold nanocages for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in vivo. Chem. Eng. J. 446, 136868 (2022).
-
Tardito, S. et al. Macrophage M1/M2 polarization and rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review. Autoimmun. Rev. 18, 102397 (2019).
-
Liu, Y. et al. Multifunctional Janus nanoplatform for efficiently synergistic theranostics of rheumatoid arthritis. ACS Nano 17, 8167–8182 (2023).
-
You, D. G. et al. Metabolically engineered stem cell–derived exosomes to regulate macrophage heterogeneity in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Adv. 7, eabe0083 (2021).
-
Rodriguez-Ramiro, I. et al. Pharmacological and genetic increases in liver NADPH levels ameliorate NASH progression in female mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 210, 448–461 (2024).
-
Weng, L. et al. Surplus fatty acid synthesis increases oxidative stress in adipocytes and lnduces lipodystrophy. Nat. Commun. 15, 133 (2024).
-
Fearon, U., Canavan, M., Biniecka, M. & Veale, D. J. Hypoxia, mitochondrial dysfunction and synovial invasiveness in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 12, 385–397 (2016).
-
Jia, N. et al. Metabolic reprogramming of proinflammatory macrophages by target delivered roburic acid effectively ameliorates rheumatoid arthritis symptoms. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 8, 280 (2023).
-
Guan, F. et al. Tissue macrophages: origin, heterogenity, biological functions, diseases and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 10, 93 (2025).
-
Wang, Z. et al. A targeted exosome therapeutic confers both CfDNA scavenging and macrophage polarization for ameliorating rheumatoid arthritis. Adv. Mater. 35, e2302503 (2023).
-
Li, L. et al. M2 macrophage-derived sEV regulate pro-inflammatory CCR2+ macrophage subpopulations to favor post-AMI cardiac repair. Adv. Sci. 10, e2202964 (2023).
-
Qiao, Y. et al. Engineered algae: a novel oxygen-generating system for effective treatment of hypoxic cancer. Sci. Adv. 6, eaba5996 (2020).
-
Wang, W. et al. Engineering micro oxygen factories to slow tumour progression via hyperoxic microenvironments. Nat. Commun. 13, 4495 (2022).
-
Zhong, D. et al. Microalgae-based hydrogel for inflammatory bowel disease and its associated anxiety and depression. Adv. Mater. 36, e2312275 (2024).
-
Ouyang, J. et al. Biomimetic nanothylakoids for efficient imaging-guided photodynamic therapy for cancer. Chem. Commun. 54, 3468–3471 (2018).
-
Chen, B., Ni, Y., Liu, J., Zhang, Y. & Yan, F. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells exert diverse effects on different macrophage subsets. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 8348121 (2018).
-
Wynn, T. A., Chawla, A. & Pollard, J. W. Macrophage biology in development, homeostasis and disease. Nature 496, 445–455 (2013).
-
Ma, C. et al. Significantly improving the bioefficacy for rheumatoid arthritis with supramolecular nanoformulations. Adv. Mater. 33, e2100098 (2021).
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by grants from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (no. 2023YFF0714200 to Z.S.), the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (no. XDB0930000 to H.Z.), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 92159304, 82372022 and 82227806 to Z.S.; nos. 82171958 and 82572255 to D.H.; no. 82271998 to Y.L.), the Shenzhen Medical Research Fund (no. B2302021 to Z.S.), the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Fund (no. 2024A1515030212 to D.G.), the Guangzhou Municipal Science and Technology Department: 2023 Key research and development plan projects (no. 2023B03J1350 to Y.L.), the Shenzhen Outstanding Talents Training Fund (to H.Z.), and the China-Singapore International Joint Laboratory for Rare Earth Imaging Materials and Devices (to Z.S.). W.T. acknowledges the support from the Harvard /Brigham Health & Technology Innovation Fund (no. 2023A004452 to W.T.), Nanotechnology Foundation (no. 2022A002721 to W.T.), and Distinguished Chair Professorship Foundation (no. 018129 to W.T.). We thank C. Liu, Y. Ren and S. Qiao for technical support with photoacoustic blood oxygenation imaging. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. We thank Shanghai Luming Biological Technology for providing proteomics services.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z. Li, Y.Y. and Y.S. conceived and designed the study. Z. Li and Y.Y. performed research. Z. Li and Y.Y. conducted the experiments. Z. Li, Y.Y., Y.S., D.H., D.G., Y.Z. and H.Y. performed data analysis. H.Q. and Y. Liu provided clinical samples. Z. Li, Z. Luo, Q.S., N.K., Y. Li, H.Z., W.T. and Z.S. wrote and revised the paper. All authors discussed the results and approved the final paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
W.T. consults for (or serves on scientific advisory boards), has lectured (and received a fee), or conducts sponsored research at Harvard Medical School/Brigham and Women’s Hospital for the following entities: Novo Nordisk A/S, Henlius USA Inc. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Nanotechnology thanks Mauro Perretti and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary key resources tables, Methods, Figs. 1–34 and primary gating strategy for the identification of macrophage subpopulations.
Source data
Source Data Fig. 1
Statistical source data.
Source Data Fig. 1f
Unprocessed western blots.
Source Data Fig. 2
Statistical source data.
Source Data Fig. 3
Statistical source data.
Source Data Fig. 4
Statistical source data.
Source Data Fig. 5
Statistical source data.
Source Data Fig. 6
Statistical source data.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Yang, Y., Shi, Y. et al. Bioengineered photosynthetic nanothylakoids reshape the inflammatory microenvironment for rheumatoid arthritis therapy.
Nat. Nanotechnol. (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-025-02063-3
-
Received:
-
Accepted:
-
Published:
-
Version of record:
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-025-02063-3

